Transmit power in a router is the strength of the signal sent from the router to the connected device. The higher the transmit power, the stronger the signal received by the device.
Routers use transmit power to determine the range and coverage of the internet signal they provide. Transmit power is measured in decibels (DBM), with higher values indicating higher transmit power. However, a higher transmit power can also cause interference with nearby signals and reduce the overall quality of the signal.
It is important to note that while increasing the transmit power may seem like a good idea, it can lead to several problems such as network congestion and decreased network performance. As such, it is crucial to find the optimal transmit power for a router to ensure the best possible internet performance and coverage.
What Is Transmit Power In Router?
Transmit power is the strength of a router’s signal. It’s the amount of energy used to boost the signal sent out by your router’s antenna. The power level varies based on different factors such as distance, obstructions, and device compatibility.
Transmit power determines how far the Wi-Fi signal emitted from your router can reach. In essence, the strength of the wireless coverage. It’s important to note that higher transmit power does not always equal better performance. The higher the power, the more interference you create with your neighbors.
This can affect your network speed. It’s recommended to adjust your router’s transmit power based on your environment and device needs. Understanding transmit power can improve the quality of your Wi-Fi signal and connectivity.
What is the Maximum Transmit Power for 2.4 GHz WiFi
When it comes to 2.4 GHz WiFi, have you ever wondered what the maximum transmit power is? It’s a question that often pops up, especially for those looking to optimize their wireless network performance. Well, the answer lies within regulatory guidelines set by different countries around the world. In the United States, for example, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has limited the maximum transmit power for 2.4 GHz WiFi devices to 1 watt (30 dBm).
But here’s where things get interesting – while 1 watt may be technically allowed in theory, most consumer-grade routers and devices actually operate at lower power levels to avoid interference with other nearby networks. This practice stems from a consideration known as EIRP or Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power, which takes into account not just the actual transmit power but also factors like antenna gain and cable loss.
In essence, your WiFi router might not be cranking out its full potential in terms of transmission power even if regulations permit it. This is because manufacturers generally optimize their devices for typical use cases and real-world scenarios while staying compliant with local regulations. So next time you check your router settings or read about impressive transmit powers on technology specifications, keep in mind that there’s more than meets the eye when it comes to unleashing the true potential of your wireless network!
How Does Transmit Power Work In Router?
Transmit power is the strength of the wireless signal sent by the router. The amount of power in the transmission affects the strength of the signal, which in turn affects the range of the wireless signal. Understanding the nature of wireless signals is important to grasp the concept of transmit power.
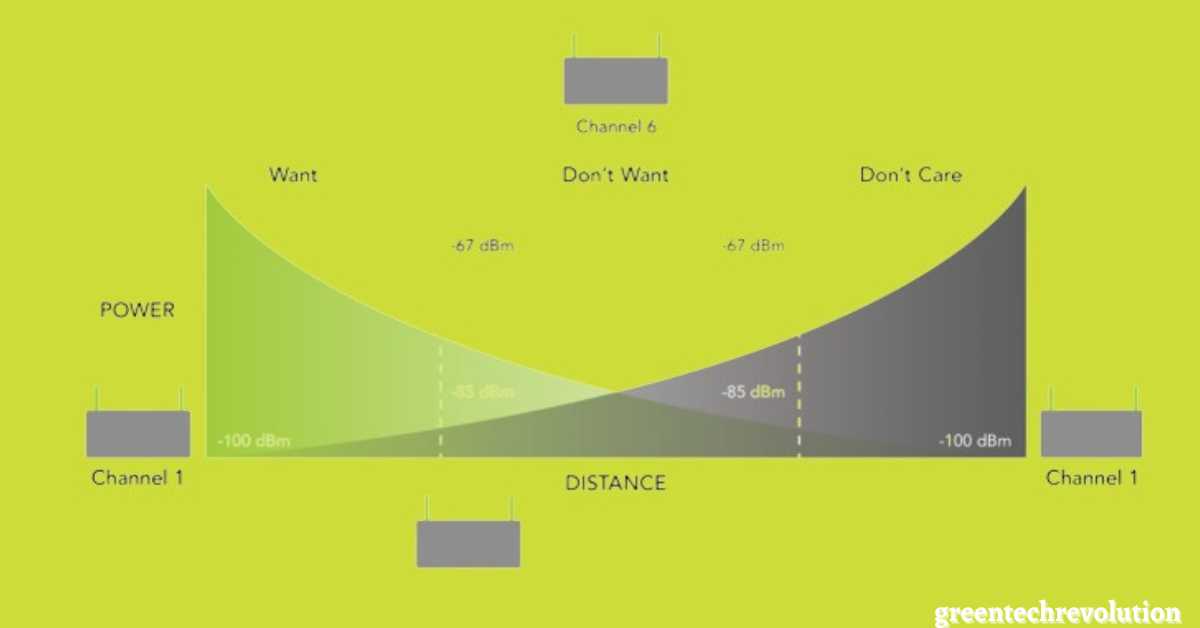
The signal strength decreases as the distance from the router increases. Transmit power helps to compensate for the strength loss, extending the wireless range. Higher transmit power can improve the signal range but also lead to interference with other wireless devices.
The correct balance between transmit power and wireless range is important for optimal performance.
Types Of Transmit Power In Router
Transmit power refers to the strength of the wireless signal that a router transmits to connect devices to the internet. There are various types of transmit power, including high, low, adjustable, fixed, dual-band, and single-band. High transmit power improves coverage but can cause interference.
Conversely, low transmit power saves energy but reduces coverage. Adjustable transmit power allows users to customize the signal strength, while fixed transmit power gives no control over signal strength. Dual-band transmit power works on both 2. 4ghz and 5. 0ghz bands, while single-band transmit power works only on one frequency.
Each power type has its pros and cons, so it’s essential to choose one that suits your needs best. For example, high transmit power is useful in large spaces, but low power may be better for a small studio.
Transmit Power And Network Performance
Transmit power plays a crucial role in the overall performance of your router and network. The more powerful the transmission strength, the better the network coverage and speed. However, high transmit power can also have certain limitations, including interference with neighboring networks and increased power consumption.
The data transfer rate is also closely linked to the transmit power, as a higher transmission strength can result in faster data transfer. It’s important to strike the right balance between transmit power and network performance to ensure optimal performance without interfering with other networks in the vicinity.
Regulatory Constraints On Transmit Power
In different countries, regulatory constraints limit the transmit power of routers. Violating these rules may result in hefty fines or legal action. The constraints are in place to prevent interference with other devices and ensure wireless communication remains reliable. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) enforces the regulations, while in Europe, it is the European Union’s radio equipment directive (red).
The consequences of violating these rules may vary, but they can include disabling the device or even imposing criminal charges in extreme cases. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the transmit power limits and use a router that complies with these constraints.
Measuring Transmit Power
Transmit power is an essential aspect of any wireless network and requires accurate measurement. Using a power meter is one of the most precise ways to measure transmit power, as it directly measures the power output. Transmit power measurements can also be done with software, which is more accessible and faster.
However, software measurements are less accurate and may not give an exact value. Interpreting transmit power measurements requires knowledge of the unit of measurement (usually DBM) and the acceptable range for the specific router. Knowing the transmit power of a router is critical when troubleshooting connectivity issues or benchmarking network performance.
Overall, understanding how to measure and interpret transmit power is an essential aspect of network setup and optimization.
Optimizing Transmit Power
Optimizing transmit power is essential to ensure you have the strongest and most reliable Wi-Fi signal possible. Factors to consider when optimizing transmit power include the size and layout of your space, the number of devices accessing your network, and the types of walls and other obstacles within your space.
Best practices for optimal transmit power include adjusting the power setting to a medium level, testing your network speed regularly, and positioning your router in an open space. However, some common mistakes to avoid when optimizing transmit power include setting the transmit power too high and failing to test your network after making changes.
By carefully considering these factors and best practices, you can optimize your router’s transmit power to enjoy optimal Wi-Fi speeds and connectivity.
Transmit Power In Different Router Brands
Transmit power in router brands such as tp-link, Netgear, and Asus vary in implementation. Some brand models offer more flexible transmit power options than others. For instance, tp-link allows users to adjust the transmit power between a wide range of values while some Asus models don’t permit any alteration.
Netgear, on the other hand, does not provide a straightforward interface for modifying the transmit power. Transmit power controls the signal’s strength that your router sends to the client device and must be taken into account when dealing with interference and extended range needs.
It is essential to know how different brands implement transmit power to improve Wi-Fi performance.
The Future Of Transmit Power In Router
Transmit power in routers is a crucial aspect of wireless communication. With emerging technologies and changing regulations, the future of transmit power is set to evolve drastically. There will be changes in regulations that govern transmit power and improvements in transmit power management.
The impact of emerging wireless technologies will also affect transmit power. As a result, it is crucial for router manufacturers to stay up-to-date with these changes to ensure their products remain compliant with regulations and effective in transmitting data. With reduced power consumption and increased efficiency, the future of transmit power in routers looks promising.
By adopting new technologies and adhering to changing regulations, router manufacturers can ensure that their products remain relevant and effective in the years to come.
Benefits Of High Transmit Power
Transmit power is an essential feature of routers that helps improve wireless connectivity. High transmit power has several advantages, including extended wireless range, better signal penetration, and improved network reliability. With increased transmit power, you can enjoy uninterrupted wireless connectivity even when you are far from your router.
Moreover, it can penetrate obstacles like walls, doors, and metal objects, and provide stable signal strength. Additionally, multiple devices can utilize the same network without performance issues. This is great news for households or offices that have many devices. Transmit power is a valuable feature that can improve your network’s performance and provide better connectivity.
Risks Of High Transmit Power
Transmit power in routers is the strength of the wireless signal that is sent out. You may think that a high power level can improve your Wi-Fi signal, but it can have negative effects. High transmit power can be a health concern, as it increases exposure to electromagnetic radiation.
Moreover, it can interfere with other wireless devices that share the same frequency range. This can cause network instability and poor signal quality. Additionally, high transmit power may breach legal regulations, leading to hefty fines or prosecution. As a result, it is important to ensure that your router is set to the recommended transmit power levels to avoid such risks.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Transmit Power In Router
What Is Router Transmit Power?
Transmit power refers to the strength at which a router is able to send wireless signals.
Why Is Transmit Power Important?
Transmit power determines the range covered by a Wi-Fi signal. The higher the power, the longer the range.
What Is The Unit Of Measure For Transmit Power?
Transmit power is measured in milliwatts (mW) or decibels-milliwatt (DBM).
Can I Adjust The Transmit Power On My Router?
Most routers allow you to adjust the transmit power. However, it’s not recommended to increase it beyond the legal limit in your country.
What Is The Legal Limit For Router Transmit Power?
The legal limit for router transmit power varies by country. Check with your local regulatory authority to find out.
Does Higher Transmit Power Always Mean Better Signal?
Not necessarily. Increasing transmit power beyond a certain level can cause interference and affect the quality of the signal.
How Can I check my router’s Transmit Power?
You can use a Wi-Fi analyzer app or a router firmware to check the transmit power of your router.
What Is The Default Transmit Power Setting On Most Routers?
The default transmits power setting on most routers is usually set to “auto”. This allows the router to adjust the power based on the signal strength needed.
How Can I Optimize My Router’s Transmit Power For Better Performance?
Ensure your router is placed in a central location, away from obstructions and interference. You can also adjust the power setting to find a balance between range and quality.
Can High Transmit Power Cause Health Risks?
There’s no conclusive evidence that high transmit power from routers causes health risks. However, it’s recommended to maintain a safe distance from the router during use.
Final Thoughts
The transmit power of a router plays a crucial role in determining the strength and range of its wireless signal. A high transmit power can help you cover a larger area, but it can also cause interference with other wireless devices.
On the other hand, a lower transmit power can reduce interference, but it may not provide enough coverage for your needs. It’s important to note that changing the transmit power also affects the overall performance of your router. Therefore, it is recommended to balance the transmit power according to your specific needs.
Knowing what is transmit power in the router and how it affects your wireless network can help you make informed decisions when setting up your home or office network. Be mindful of the factors that can influence its performance and find the balance that works best for you.
Regularly monitoring and adjusting the transmit power can ensure that your network remains strong and stable, providing a seamless online experience for you and your devices.








Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.