A Wi-Fi router works by taking an internet signal from your modem and broadcasting it wirelessly to other devices in your home or office. In today’s digital era, wi-fi is an essential tool for everyday life.
Wi-fi technology makes it possible to connect to the internet, access information, and communicate with others without any cables or cords. However, have you ever wondered how wi-fi works and how it transmits signals to your devices? This is where a wi-fi router comes into play.
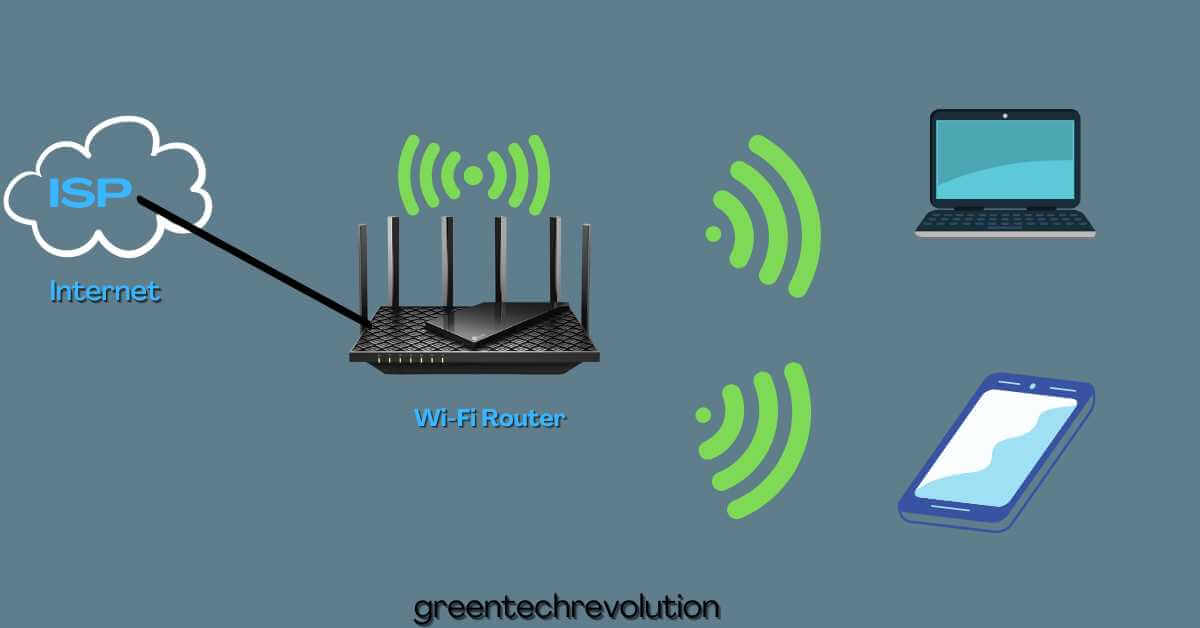
A wi-fi router acts as a central hub that connects to a modem and distributes an internet signal wirelessly to multiple devices. It uses radio waves to communicate with your devices, allowing you to browse the web, stream videos, and access online services. Understanding how a wi-fi router works is essential for optimizing your internet connection and ensuring reliable and fast internet access.
What Is A Wi-Fi Router? The Core Functionality.
A wi-fi router is a device that connects your electronic devices to the internet. It helps you to send and receive data wirelessly, increasing mobility and flexibility in your home or office. While wi-fi routers are becoming increasingly common in today’s world, not many of us fully understand how they work.
We will discuss the core functionality of a wi-fi router, demystifying how it functions to keep you connected.
A Brief Introduction To The Purpose Of A Wi-Fi Router.
Before we dive into the primary function of a wi-fi router, let’s look at a few interesting facts about its purpose.
- A wi-fi router typically works within a range of 150 ft (46 meters) in a home setting and up to 1000 ft (305 meters) in an open area.
- Wi-fi routers use radio waves that operate at either 2.4ghz or 5ghz frequencies to transmit signals.
- The term “wi-fi” stands for “wireless fidelity,” a brand name created by some members of the wi-fi alliance to market wireless local area network (wlan) technology.
Discussing The Primary Function Of A Wi-Fi Router
There are a few different functions that a router can perform, but we will focus on the primary function, which is to connect all of your devices to the internet wirelessly. Let’s take a closer look at this function:
- A wi-fi router allows you to connect multiple devices to the internet wirelessly and simultaneously. This includes smartphones, laptops, tablets, and even gaming consoles.
- The router receives data from your modem and wirelessly transmits it to your electronic devices using radio waves, which are invisible but high-frequency electromagnetic waves.
- It also uses a unique identifier, known as the service set identifier (ssid), so that your electronic devices can connect to the correct network.
- Wi-fi routers have security features such as encryption to ensure that only authorized users have access to the network, protecting your sensitive information from hackers and other malicious actors online.
A wi-fi router has become an essential device in modern homes and offices, providing wireless connectivity, and enabling us to work and play more efficiently. By better understanding its core functionality, we can troubleshoot any issues that may arise, and appreciate the convenience that it provides.
How Does A Wi-Fi Router Work? Inside The Box.
An Overview Of The Components That Make Up A Wi-Fi Router
A wi-fi router contains a variety of different parts that work together to provide wireless internet access. Here are the essential components:
- Cpu (central processing unit): This is the brain of the router that manages all operations.
- Flash memory: This stores the router’s firmware, which provides the operating instructions.
- Ram (random access memory): This provides temporary memory for the router’s functions. Ram is necessary for carrying out processes quickly.
- Signal amplifiers: These amplify the signals so that they can reach greater distances.
- Antennas: These transmit and receive signals to and from the devices connected to it. They are usually detachable.
- Ethernet ports: These connect the router to devices using a wired connection.
- Wireless radios: These transmit and receive signals using radio waves that are used to connect wireless devices.
Explanation Of How These Components Work Together To Enable Wireless Internet Access
All these components are integrated together to connect devices to the internet without requiring any cables. Here are some key points about how these components work together:
- The router generates signals and sends them via radio waves to other wireless devices by using wireless radios.
- Extracting internet signals from ethernet cables requires signal amplifiers.
- The cpu is the brain of the router and controls all its other components.
- The antennas are responsible for transmitting and receiving signals to and from the devices.
- The firmware is stored in the flash memory and includes the instructions that tell the router how to network devices.
How Does A Router Connect To The Internet And Distribute The Signal To Devices Connected To It?
A router is required to connect to the internet so that it can enable internet access for all the devices connected to it. Here’s how a router connects to the internet and distributes the signal:
- A router connects to the internet through a broadband modem.
- The broadband modem connects to the internet service provider (isp) that provides internet access to the router.
- Once connected to the isp, the router gets an ip address, which identifies it on the internet.
- After that, the router uses this internet connection to distribute the signals to all wireless and wired devices connected to it.
Working Of Wi-Fi Signal
Wi-fi routers have become an essential part of our daily lives. They use radio waves to make a connection between your device and the internet. But, have you ever wondered how does a wi-fi router work? In this blog post, we will discuss the working of a wi-fi signal, including the difference between traditional and wi-fi routers.
Understanding The Difference Between Traditional Router And Wi-Fi Routers.
Traditional routers, also known as wired routers, connect one device to the internet using an ethernet cable. On the other hand, wi-fi routers use radio waves to connect multiple devices to the internet simultaneously. Wi-fi routers also come equipped with advanced security features to protect your devices against cyber attacks.
How Does Wi-Fi Signal Transmit Data?
To understand how a wi-fi signal transmits data, you need to know about radio waves. Wi-fi routers transmit data using radio waves, which are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. These waves are similar to those used by radios, cell phones, and televisions.
Here’s how a wi-fi router transmits data using radio waves:
- First, your device sends a request to the wi-fi router to connect to the internet.
- The wi-fi router receives the request and sends a signal in the form of radio waves.
- Your device receives the signal and then converts it back into the data it needs to access the internet.
- The data is then sent back to the wi-fi router, which sends it to the internet service provider (isp).
- The isp receives the data and sends it back to the wi-fi router using radio waves.
- The wi-fi router receives the data and sends it back to your device.
All of this happens in a matter of seconds, which is why you can browse the internet seamlessly without any interruptions.
Wi-fi routers use radio waves to connect multiple devices to the internet and transmit data wirelessly. They have become an essential part of our daily lives, making it easier for us to access the internet from anywhere in our homes.
With advanced security features and the ability to connect multiple devices, wi-fi routers have become a must-have device for everyone who uses the internet.
Frequency Bands Used In Wi-Fi Router
Wi-fi routers are a fundamental part of our daily life, but not many of us know how these devices work. Have you ever wondered how wi-fi signal magically appears on our devices and connects us to the internet? If yes, let’s dive into the world of frequency bands used in wi-fi routers.
An Explanation Of The Two Frequency Bands Used In Wi-Fi Routers
Wi-fi routers use radiofrequency bands to transmit and receive data signals. The two major frequency bands used in wi-fi routers are 2. 4 ghz and 5 ghz. Let’s have a closer look at each of them:
2.4 Ghz Frequency Band
The 2. 4 ghz frequency band has been around since the inception of wi-fi routers. It is widely used in various wireless technologies such as bluetooth, cordless phones, and microwaves. The key points about the 2. 4 ghz frequency band are:
- It has a longer range, making it suitable for larger areas such as home and office.
- The 2.4 ghz frequency band is susceptible to interference from other wireless devices that operate on the same frequency.
- It can handle fewer devices at once because of the limited bandwidth.
5 Ghz Frequency Band
The 5 ghz frequency is a relatively new technology introduced to wi-fi routers. It offers faster internet speeds and bandwidth than the 2. 4 ghz frequency band. The key points about the 5 ghz frequency band are:
- It provides faster speed with less congestion, making it ideal for streaming hd content and playing online games.
- The 5 ghz frequency band has a shorter range than the 2.4 ghz frequency band, making it suitable for smaller areas.
- Wi-fi routers that use 5 ghz frequency bands can handle multiple devices simultaneously without compromising speed.
Understanding The Difference Between 2.4 Ghz And 5 Ghz Frequencies
The primary difference between the 2. 4 ghz and 5 ghz frequency bands is the internet speed, range, and the number of devices that can be connected at once. Here are some key differences between the 2. 4 ghz and 5 ghz frequency bands:
- The 5 ghz frequency band offers faster internet speeds than the 2.4 ghz frequency band because it has more bandwidth.
- The 2.4 ghz frequency band has a longer range than the 5 ghz frequency band, making it suitable for larger areas such as offices and homes.
- Many older devices may not support the 5 ghz frequency band, but they will work with the 2.4 ghz frequency band.
The Impact Of Frequency Bands On Speed And Range Of Wireless Network
The frequency band used by your wi-fi router has an impact on the speed and range of your wireless network. Here are some important things to remember:
- If you have a large house or office, consider using a wi-fi router with a 2.4 ghz frequency band to ensure coverage everywhere.
- If you want faster internet speeds or have multiple devices that require high bandwidth, opt for a wi-fi router that uses a 5 ghz frequency band.
- Some wi-fi routers use both frequency bands, so you get the best of both worlds.
Understanding the different frequency bands used in wi-fi routers is crucial in selecting the right one that meets your needs. Whether it’s the 2. 4 ghz frequency band with longer reach or the 5 ghz frequency band with higher internet speeds, choose the right one to enjoy seamless connectivity and faster internet speeds.
Wi-Fi Standards And Their Differences
Wi-fi is a wireless technology that allows electronic devices to connect to each other and the internet without the need for cables. Wi-fi works by using radio frequencies to transmit data between devices. However, not all wi-fi connections are created equal.
There are several different wi-fi standards, each with its own unique features and capabilities. In this section, we’ll explain the different wi-fi standards and their differences.
Explanation Of The Different Wi-Fi Standards
The wi-fi standards have been evolving over time. The older standards provided slower data transfer rates, while the newer standards provide faster speeds. The following are the different wi-fi standards.
- 802.11a: This standard was released in 1999 and operates on a 5 ghz frequency band. It provides a maximum speed of 54 mbps.
- 802.11b: This standard was also released in 1999 and operates on a 2.4 ghz frequency band. It provides a maximum speed of 11 mbps.
- 802.11g: This standard was introduced in 2003 and operates on a 2.4 ghz frequency band. It provides a maximum speed of 54 mbps.
- 802.11n: This standard was released in 2009 and operates on both 2.4 ghz and 5 ghz frequency bands. It provides a maximum speed of 600 mbps.
- 802.11ac: This standard was introduced in 2013 and operates on 5 ghz frequency bands. It provides a maximum speed of more than 1 gbps.
Understanding The Differences Between 802.11 A/B/G/N/Ac
As you can see, the differences between the wi-fi standards relate to their frequencies, bandwidths, and maximum speeds. The “a” and “ac” standards operate on the 5 ghz frequency band, which is less congested than the 2. 4 ghz band.
This means that these standards offer less interference and faster speeds. The “b” and “g” standards operate on the 2. 4 ghz band, which is more congested, resulting in slower speeds and more interference. However, the “b” standard is still popular in some regions due to its compatibility with older devices.
The “n” standard is a significant improvement over the earlier standards as it operates on both 2. 4 ghz and 5 ghz frequency bands, allowing for faster speeds and increased bandwidth. In comparison, the “ac” standard provides even faster speeds and improved performance.
It has a greater range and capacity to deliver better internet signals throughout your home, making it perfect for streaming high-quality videos and playing online games.
How Each Wi-Fi Standard Affects Network Performance
The wi-fi standard you choose can have a significant impact on your network’s performance. The higher the standard, the faster and more reliable your internet connection will be. For example, if you have a lot of devices in your home that require a fast and reliable connection, it’s best to go with the latest “ac” standard.
On the other hand, if you have older devices that can only connect to an older standard, it’s best to stick with that standard.
Understanding the different wi-fi standards is crucial for selecting the right router and ensuring the best internet performance possible. By choosing the appropriate standard, you can get faster speeds, better range, and more reliability, making your online experience more enjoyable and efficient.
Network Security And Encryption
Your wi-fi router, the device responsible for the wireless connection in your home, offers you the convenience of being able to connect to the internet wirelessly. However, with the freedom and ease come risks to your online security. That’s why you need to take network security and encryption seriously to protect your communication.
Here’s a breakdown of how you can safeguard your online security.
The Importance Of Securing Your Wireless Network With Strong Passwords And Encryption.
To protect your online communication, you need to secure your wireless network by creating strong passwords and encrypting data. Here are the key points to keep in mind:
- Change your router’s default administrator username and password because attackers often know them.
- Keep your router’s firmware up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities that hackers may exploit.
- Always use a strong password, preferably 12 characters long with uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable wi-fi protected access 2 (wpa2) security, which provides more robust data encryption than wired equivalent privacy (wep) and can prevent unauthorized access to your network.
Understanding The Different Types Of Network Encryptions And Security Protocols.
Wireless network transmissions use various encryption protocols to protect your data as it passes over the airwaves. Here are the encryption protocols you need to know:
- Wired equivalent privacy (wep): This was the first security protocol for wireless networks but is no longer considered secure due to its weak encryption.
- Wi-fi protected access (wpa): Wpa has improved encryption and addressed some of the flaws in wep, but it’s still vulnerable to some attacks.
- Wi-fi protected access 2 (wpa2): This is the latest and most secure wireless security protocol available. It uses advanced encryption standard (aes) encryption to provide robust protection against hackers and intruders.
Securing your wireless network with strong passwords and encryption is crucial to safeguard your online security. Remember to use strong passwords, change the default login credentials, update your router’s firmware, and optimize your encryption protocols to protect your communication.
Placement Strategies
Wi-fi routers are essential for home or workplace wireless connectivity. Since we rely on them for internet access, it is crucial to ensure that the device works efficiently. A well-placed wi-fi router ensures that you have strong, reliable signals, but if positioned haphazardly, the opposite is true.
In this blog post, we will explore how the placement of your wi-fi router affects performance and provide tips on the best locations for optimum reception and transmission.
How The Placement Of Your Wi-Fi Router Affects Performance
The placement of your wi-fi router plays a critical role in determining its performance. The closer it is to where you access the internet, the stronger the signal will be. Here are some key points to consider:
- The signal emanates from the router in all directions. Find the most central location for the device to ensure signals reach all areas of the home or workspace.
- Avoid placing the router near reflective surfaces, such as metallic surfaces, mirrors, or glass. These materials can reflect and redirect the signals, which can result in weak signals or dead spots in certain areas of the home or office.
- Other electronic devices such as microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors emit signals that can interfere with the wi-fi signal. Place the router as far away as possible from these devices to avoid performance issues.
- The height of your wi-fi router affects its performance. Placing it on a high surface such as a shelf or mounting it on a wall, ensures that signals travel further.
- Always keep your router software updated to ensure that it performs optimally. Outdated firmware can lead to compatibility issues and slow performance.
Tips On The Best Locations For Optimum Reception And Transmission
Choosing the right location ensures that your wi-fi router performs optimally. Here are some tips for best placement:
- Place the router near the center of the house or office for optimal signal distribution.
- Position the router away from metallic surfaces, mirrors, and glass.
- Ensure that the router is at least 3-6 feet away from other electronic devices that may interfere with the signals.
- Mount the router on the wall for maximum signal range.
- Position the antennas facing upwards and ensure that they are perpendicular to the ground.
- Ensure that the router is not placed in an enclosed space such as a cabinet or drawer.
- If you live in a multi-story building, consider placing the router on the upper floors for better signal distribution.
The placement of your wi-fi router is crucial for its optimal performance. Ensure that you follow these placement strategies to get the most out of your wi-fi connection.
Firmware And Software Updates
How Does A Wi-Fi Router Work?
If you’re reading this blog post, you’re probably interested in finding out how a wi-fi router works. A wi-fi router is a device that enables you to connect to the internet wirelessly. It connects to a modem that receives data via an internet service provider (isp).
A wi-fi router provides you with wireless coverage throughout your home, office, or any other space where you need it. In this post, we’ll talk about firmware and software updates, and why you should keep your wi-fi router up to date.
The Importance Of Keeping Your Wi-Fi Router Up To Date With Software And Firmware Updates
Just like any other device, your wi-fi router requires software and firmware updates to run smoothly. These updates are essential as they fix bugs, improve security, and provide new features. Here are some reasons why you should ensure your wi-fi router is up to date:
- Security: Firmware updates help fix known vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. These vulnerabilities can allow hackers to access your router, steal your personal information, and even launch cyber attacks on your network.
- Improved performance: Software updates can fix bugs that may be causing network problems or slow internet speeds. These updates can also improve the performance of your router by enhancing its functionality.
- New features: Many firmware and software updates come with new features that can enhance your overall experience. These features can include parental controls, guest network access, and so on.
Steps On How To Check And Install Firmware And Software Updates On Your Wi-Fi Router
Most manufacturers release updates for their wi-fi routers periodically. Here are some steps you can take to check and update your firmware and software:
- Step 1: Go to your router’s configuration page by typing the ip address into your web browser’s address bar. You can find the ip address in the manual that came with your router or by searching online for the manufacturer’s website.
- Step 2: Once you access the configuration page, look for a section that says “firmware updates” or “software updates.”
- Step 3: Click on the “check for updates” button.
- Step 4: If there are any new updates available, download and install them.
It’s important to note that the steps to update your router may vary depending on the manufacturer and model. Always check your router’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for detailed instructions.
Updating your wi-fi router is essential to ensure that it remains secure, performs well, and provides the latest features. With these simple steps in mind, you can easily check and update your firmware and software, keeping your wi-fi router up to date and your network safe.
Bandwidth Management Techniques
Wi-fi routers have become an essential part of our daily lives, as we rely on them to connect our devices to the internet. One of the crucial aspects of any router is the bandwidth management techniques that help allocate and manage the network’s traffic efficiently.
In this section, we will delve into the two key aspects of network management: allocating bandwidth to specific devices and managing bandwidth in multiple devices and traffic.
How To Allocate Bandwidth To Specific Devices On Your Network
Wi-fi routers can allocate bandwidth to specific devices on your network using quality of service (qos) settings. Qos allows the router to prioritize certain types of traffic or devices over others, ensuring that critical traffic, such as video calls or online gaming, gets priority over non-essential traffic like downloads or web browsing.
Here are some key points to keep in mind when allocating bandwidth using qos settings:
- Qos settings can be configured in the router’s admin panel accessed via a web browser.
- Qos settings are often categorized based on the type of traffic, such as voice or video calls, gaming, or downloads.
- The qos settings allow you to set priority levels for different types of traffic, which can be helpful if you have specific devices on your network that require higher priority levels than others.
Managing Bandwidth In Multiple Devices And Traffic
Managing bandwidth in multiple devices and traffic is a critical aspect of network management, especially in households with several connected devices. Here are some key points to keep in mind when managing bandwidth:
- Some routers come with built-in features such as load balancing, which distributes network traffic over multiple devices, ensuring that no single device is hogging the entire network’s bandwidth.
- You can also use third-party software applications to monitor and manage your network’s traffic, such as netbalancer or glasswire.
- You can limit the bandwidth for specific devices or applications to prevent them from using too much bandwidth, which can slow down other devices on the network.
Wi-fi routers have become an essential component of our daily lives, and managing bandwidth is a crucial aspect of their functionality. With a basic understanding of qos settings and network management techniques, you can ensure that your network runs smoothly and efficiently, without any hiccups.
Common Wi-Fi Router Issues
A wi-fi router is a device that enables internet access through wireless connectivity. It is a crucial piece of technology that keeps us connected to the online world. Unfortunately, like all technology, wi-fi routers are not infallible and can experience problems that affect their performance and ultimately, our internet experience.
In this post, we will explore the most common wi-fi router issues, how to identify them, and steps you can take to prevent and solve them.
Overview Of The Most Common Wi-Fi Router Problems
- Slow internet speeds: Slow internet speeds are a common issue that can be attributed to a wide range of factors, including distance from a router, network congestion, and interference from other devices.
- No internet connection: A no-internet connection is a common issue that can be caused by different factors, including incorrect login credentials, modem problems, and incorrect router configuration.
- Weak wi-fi signals: A weak wi-fi signal is a common issue that can be attributed to different factors, such as obstructions, distance from a router, and interference from other devices.
How To Identify, Prevent, And Solve Issues
- Slow internet speeds:
- Check your internet speeds: Do a speed test to determine your internet speed. If it’s lower than usual, contact your internet service provider.
- Place your router in the right position: Ensure that you position your router in a central location, free from obstructions and away from other electronics that may cause interference.
- Update your firmware: Keeping your router firmware updated ensures that you have the latest features and security patches that can help improve your router’s performance.
- No internet connection:
- Check your wi-fi network name and password: Incorrect login credentials are a common issue for no internet connection. Make sure you have the right login credentials.
- Reset your router: If you have exhausted all other options, you can reset your router to its default settings. This will delete any custom configurations and restore it to its original settings.
- Weak wi-fi signals:
- Reposition your router: Ensure that you place your router in a central location, away from obstructions and other devices that may interfere with the wi-fi signal.
- Upgrade your router: If all else fails, consider upgrading your router to a newer and more powerful model that can provide faster speeds and a stronger wi-fi signal.
Wi-fi router problems are common and can have a significant impact on our internet experience. However, by taking the above steps, you can easily identify, prevent, and solve these issues, and enjoy uninterrupted internet connectivity.
Steps To Optimize Wi-Fi Network
How Does A Wi-Fi Router Work?
Wi-fi routers are essential devices that connect multiple devices to a network providing wireless internet connectivity and transmitting data packets from one device to another. These routers are made up of several components that work effortlessly to provide seamless internet connectivity.
To ensure the optimal performance of your wi-fi network, here are some steps you can follow:
Changing The Router Position
It is essential to place the router in a central location and not in a closed-off room or cupboard. In addition, it should be kept away from electronic devices such as televisions and microwave ovens to avoid interference.
Changing The Wireless Channel
Routers use broadcast channels to transmit signals to devices. It may result in congestion if more than one router uses the same channel. Changing the wireless channel on the router settings can help fix this problem.
Upgrading Router Firmware
Updating the firmware enhances the router’s performance and security. A firmware upgrade can fix bugs and add new features, leading to improved wi-fi connection speeds.
Switching The Wi-Fi Band
Routers work in two bands, 2. 4ghz and 5ghz. The 2. 4ghz band has a more extended range but is slower than the 5ghz band, which has a shorter range but higher speeds. Switching between these bands can improve the wi-fi speed and range.
Troubleshooting Steps To Identify And Fix Underperforming Networks
Here are some measures to consider when fixing slow wi-fi networks:
Restarting The Router
Sometimes, the router may experience temporary glitches and may need a reboot. Turn off the router, wait for 10 seconds and turn it back on.
Limiting Connected Devices
Too many connected devices can slow down the network. Disconnecting inactive devices or limiting the maximum number of connections can help optimize the network.
Updating The Network Drivers
Often, slow wi-fi connections are due to outdated network drivers. Updating them to the latest versions can speed up the network.
Resetting The Router
If other solutions do not work, resetting the router to factory settings can resolve the problem. However, remember to backup router configurations before resetting.
Tips For Preventing Wi-Fi Router Issues In The Future
Securing The Network
Securing the wi-fi network with a strong password can prevent unauthorized access. It also ensures that the network bandwidth is reserved for legitimate devices.
Regular Maintenance
Frequently cleaning the router, checking the cable connections, and routinely updating the router firmware can prevent router issues.
Investing In Quality Routers
High-quality routers are less prone to issues and provide better performance than the cheap ones. Investing in a robust router may seem expensive upfront, but it will pay off in the long run.
Wi-fi routers are crucial devices that provide wireless internet connectivity to numerous devices. Following the best practices mentioned above can help in optimizing the connection speed, avoid network issues and enhance the wi-fi network’s overall performance.
Wi-Fi Router Alternatives
In today’s world, we are highly dependent on the internet, and wi-fi routers have become an essential component of our daily lives. However, if you live in an area with limited connectivity or you’re always on the go, a wi-fi router might not serve your needs in the best way.
Fortunately, there are alternatives available that you can consider. In this section, we will discuss some of the wi-fi router alternatives that can help keep you connected.
Comparing The Alternatives To Wi-Fi Routers (Such As Cellular Data Plans)
If you’re on the lookout for alternatives to wi-fi routers, cellular data plans might be the first thing you think of. While cellular data plans provide an internet connection, they work differently than wi-fi routers. Let’s consider cellular data plans as an alternative to wi-fi routers and review their pros and cons.
Pros Of Cellular Data Plans
- Accessible: A cellular data plan allows you to connect to the internet anywhere you have a cellular signal. This makes them particularly useful for people who travel a lot or live in rural areas where wi-fi networks may not be available.
- No need for wi-fi network setup: With a cellular data plan, you don’t have to worry about setting up a wi-fi network, a router, or a modem.
- Multiple device access: With a cellular data plan, you can connect multiple devices like tablets, smartphones, and laptops to the internet without the need for additional hardware.
Cons Of Cellular Data Plans
- Limited data usage: Cellular data plans typically come with a data cap, and exceeding it can come with hefty overage charges.
- Signal strength: If you’re in an area without a good cellular signal, you might not be able to connect to the internet, or the connection might drop frequently.
- Slower speeds: Cellular data plans don’t always provide the same speed as wi-fi networks, which can limit your online activities.
Overall, cellular data plans can be a great alternative to wi-fi routers if you’re someone who is always on the go or lives in a remote area. However, you should weigh the pros and cons of cellular data plans before deciding whether they are the right choice for you.
Frequently Asked Questions On How Does A Wi-Fi Router Work?
How Does A Wi-Fi Router Work?
A wi-fi router sends and receives data between devices, creating a wireless network.
What Is The Purpose Of A Wi-Fi Router?
A wi-fi router allows multiple devices to connect to the internet wirelessly.
How Do I Connect To A Wi-Fi Router?
Find the wi-fi network name and password provided by the router and enter it on your device.
What Type Of Devices Can Connect To A Wi-Fi Router?
Any device with wi-fi capabilities, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, can connect to a wi-fi router.
Why Is My Wi-Fi Router Slow?
Wi-fi speed can be affected by the distance between the router and device, interference, and the number of devices connected.
How Do I Secure My Wi-Fi Router?
Set a strong password, enable wpa2 encryption, and turn off remote management to secure your wi-fi router.
Is It Safe To Use Public Wi-Fi?
Public wi-fi can be unsafe as hackers can intercept your data. Use a vpn to encrypt your data and protect your privacy.
How Do I Reset My Wi-Fi Router?
Press and hold the reset button on the back of the router for 10 seconds to reset it to factory settings.
Can I Use A Wi-Fi Router Without An Internet Connection?
Yes, you can use a wi-fi router without an internet connection to create a local network for file sharing and gaming.
How Do I Troubleshoot My Wi-Fi Router?
Restart your router, update firmware, and fix interference issues to troubleshoot your wi-fi router.
Final Thoughts
A wi-fi router is a crucial device that allows multiple devices to connect to the internet simultaneously. Routers transmit data packets wirelessly through radio waves, utilizing different frequency bands. The router acts as a “traffic cop” for internet traffic, directing the data packets to their intended destinations.
This process ensures that each connected device receives the data it needs. Wi-fi routers have evolved over time to handle higher data volumes, faster speeds, and improved security. Enhancements like mimo and beamforming enable routers to provide a stronger signal to devices located farther away.
With an understanding of how a wi-fi router works, you can optimize your wireless network and ensure that each device receives the fastest and most reliable connection available. By staying informed about the latest developments in wi-fi router technology, you can stay ahead of the curve and enjoy the benefits of a fast and efficient wireless network.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.